
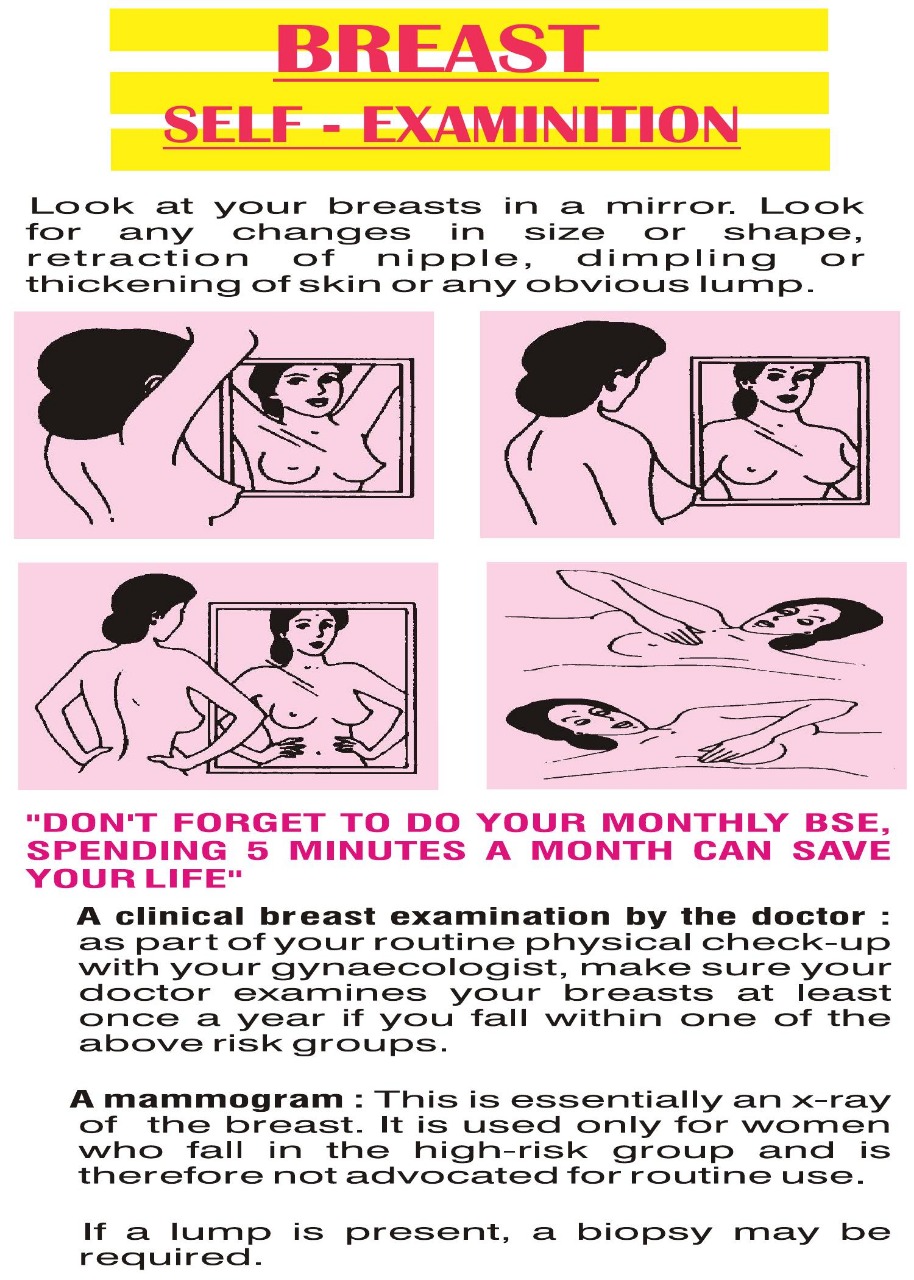
Breast Self-Examination
Cancer in Women
Overview
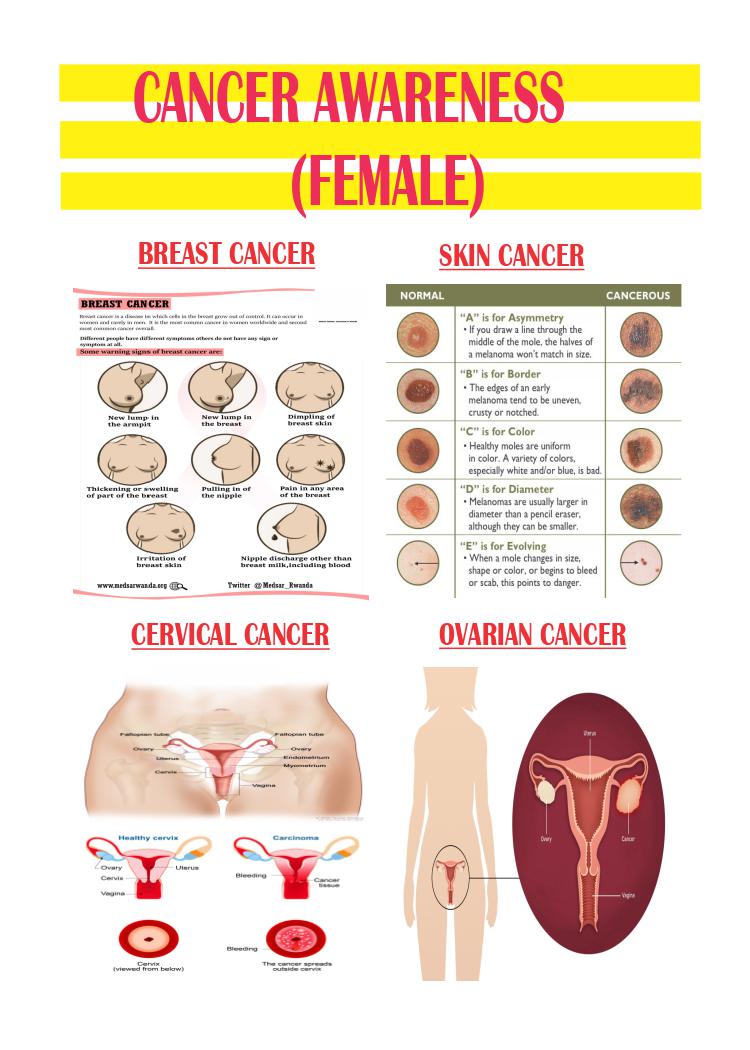
Some of the cancers that most often affect women are breast, colorectal, endometrial, lung, cervical, skin, and ovarian cancer. Knowing about these cancers and what you can do to help prevent them or find them early may help save your life.
What is Cancer?
You are made up of trillions of cells that normally grow and divide as needed. Cancer starts when cells grow uncontrollably, crowding out normal cells, making it hard for your body to function properly.
Cancer Stages
Cancer staging determines how large the cancer is and whether it has spread. Lower stages (1 or 2) indicate less spread, while higher stages (3 or 4) mean more spread, guiding treatment decisions.
Types of Cancer
Hematologic (Blood) Cancers: Include leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma.
Solid Tumor Cancers: Include breast, prostate, lung, and colorectal cancers.
What is a Tumor?
A tumor is a lump or growth. Benign tumors are not cancerous, while malignant tumors are cancerous.
Causes of Cancer
Cancer develops due to multiple genetic changes, influenced by lifestyle, inherited genes, or environmental factors. Often, no clear cause is identified.
How Cancer Spreads
Cancer cells can spread through the bloodstream or lymph system, a process called metastasis. They must undergo several changes to grow in new areas of the body.
Our Objectives
- Raise awareness about cancer in women.
- Detect signs and symptoms of oral, breast, and cervical cancer.
- Provide vital treatment for detected cancers.
- Reduce the number of cancer patients in society.
- Fund treatment for patients below the poverty line.
Cancer Prevention Tips
- Maintain oral and genital hygiene.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins A and C.
- Avoid oily, spicy, pickled, or barbecued foods.
- Prefer vegetarian foods.
- Exercise regularly and control weight.
- Get vaccinated (HBsAg, HPV).